The latest version of the Leads4pass 300-410 dumps includes 925 exam questions and answers (with the latest 2025 simulated labs). Outdated technologies have been removed, and new exam technologies compliant with have been added, making it ideal for candidates preparing for the 300-410 ENARSI exam.
Download the latest version of the 300-410 dumps here: https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html (including the latest 2025 simulated labs), and practice 300-410 ENARSI exam questions using the PDF exam file and VCE exam simulator to help you succeed.
Check out the Cisco 300-410 PDF available free of charge in 2025:
This content is from my latest edit for 2025, including the latest exam questions and answers from January and August.
[Jan 2025]: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1BYgvye3t0PrKhTo6eI1jB-FuY-_H6Zdw/view?usp=drive_link
[Aug 2025]:https://drive.google.com/file/d/1D7hNE-ws0XTk0o6caQo9CPg1BtR3wdWp/view?usp=sharing
Check out the Cisco 300-410 dumps exam questions and answers provided in the new version (including 2025 Newest Simulation Labs):
| Number of exam questions | Exam name | Release time | From |
| 15 (Free) | Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI) | Aug 28,2025 | Leads4Pass |
2025 Questions 1:
Refer to the exhibit.TCP traffic should be reaching host 10.10.10.10/24 via R2. Which action resolves the issue?
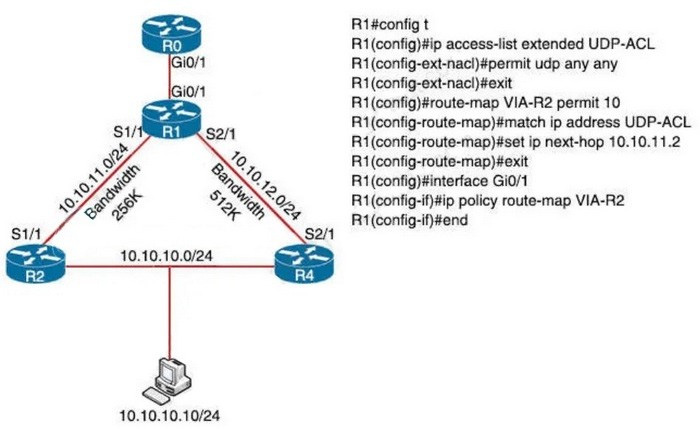
A. Allow TCP in the access list with no changes to the route map.
B. Set IP next-hop to 10.10.12.2 under the route-map permit 10 to allow TCP traffic.
C. Add a permit 20 statement in the route map to allow TCP traffic.
D. TCP traffic will reach the destination via R2 without any changes.
Correct Answer: A
If we add a “permit 20” statement in the route-map then we will allow other traffic to pass through (in fact Policy-based routing allows other traffic to pass through by default).
But the bandwidth of R1-R4 is higher than that of R1-R2 so TCP traffic might go through R4 instead of R2. Therefore we should allow TCP in the ACL so that TCP traffic is forwarded via R2.
2025 Questions 2:
Refer to the exhibit.

Not all connected and static routes of router B are received by router A even though EIGRP neighborship is established between the routers. Which configuration resolves the issue?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Correct Answer: D
2025 Question 3:
What are two purposes of using IPv4 and VPNv4 address-family configurations in a Layer 3 MPLS VPN? (Choose two.)
A. RD is prepended to the IPv4 route to make it unique.
B. The VPNv4 address consists of a 64-bit route distinguisher that is prepended to the IPv4 prefix.
C. MP-BGP is used to allow overlapping IPv4 addresses between customers to advertise through the network.
D. The IPv4 address is needed to tag the MPLS label.
E. The VPNv4 address is used to advertise the MPLS VPN label.
Correct Answer: AB
VPNv4 address consists of 64-bit Route Distinguisher (RD) prepended to IPv4 prefix. This is to make routes unique that are in different VRFs.
2025 Question 4:
Refer to the exhibit.
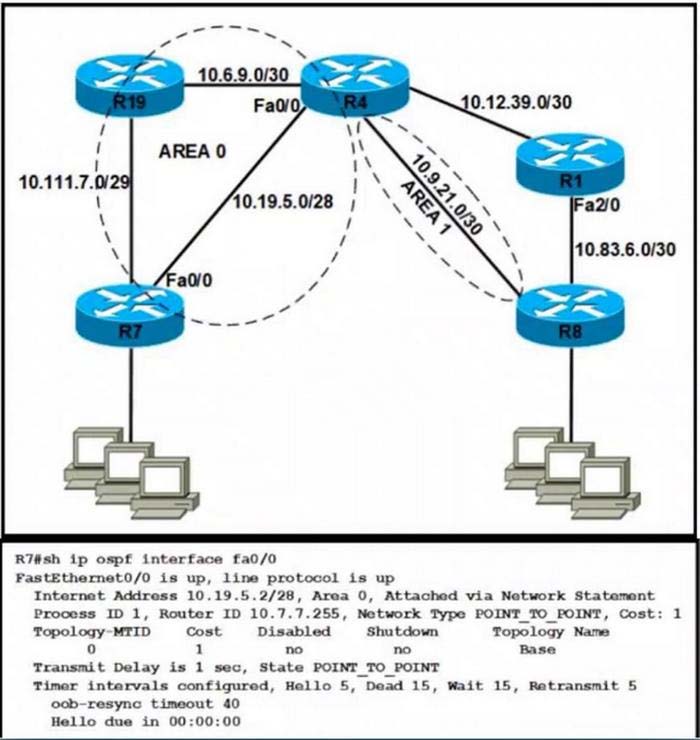
Router R4 is configured correctly with default OSPF values. A network engineer configured R7 for OSPF. R7 must not be elected as a DR for the segment between R4-R7. The adjacency between R4 and R7 failed to form. Which configuration resolves the issue?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Correct Answer: C
2025 Question 5:
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the packet types from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
Select and Place:
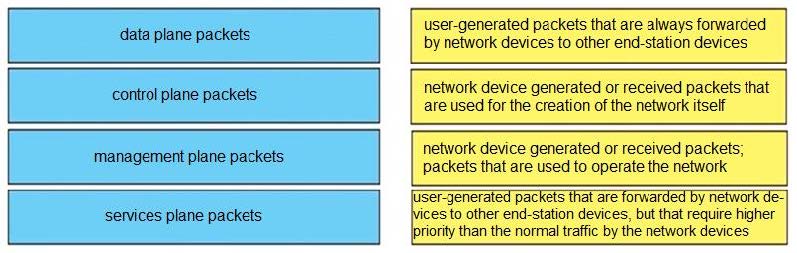
Correct Answer:
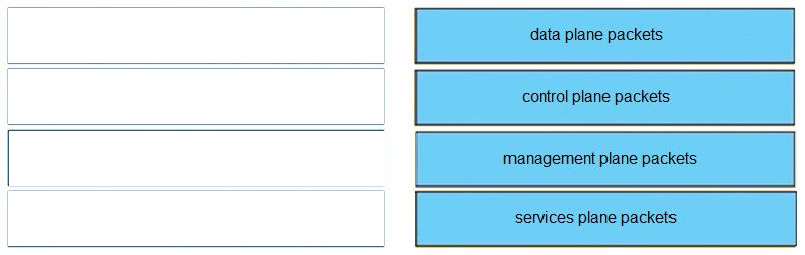
Unlike legacy network technologies such as ISDN, Frame Relay, and ATM that defined separate data and control channels, IP carries all packets within a single pipe. Thus, IP network devices such as routers and switches must be able to distinguish between data plane, control plane, and management plane packets to treat each packet appropriately. From an IP traffic plane perspective, packets may be divided into four distinct, logical groups:
1.
Data plane packets -End-station, user-generated packets that are always forwarded by network devices to other end-station devices. From the perspective of the network device, data plane packets always have a transit destination IP address and can be handled by normal, destination IP address- based forwarding processes.
2.
Control plane packets -Network device generated or received packets that are used for the creation and operation of the network itself. From the perspective of the network device, control plane packets always have a receive destination IP address and are handled by the CPU in the network device route processor. Examples include protocols such as ARP, BGP, OSPF, and other protocols that glue the network together.
3.
Management plane packets -Network device generated or received packets, or management station generated or received packets that are used to manage the network. From the perspective of the network device, management plane packets always have a receive destination IP address and are handled by the CPU in the network device route processor. Examples include protocols such as Telnet, Secure Shell (SSH), TFTP, SNMP, FTP, NTP, and other protocols used to manage the device and/or network.
4.
Services plane packets -A special case of data plane packets, services plane packets are also user- generated packets that are also forwarded by network devices to other end-station devices, but that require high-touch handling by the network device (above and beyond normal, destination IP address-based forwarding) to forward the packet.
Examples of high-touch handling include such functions as GRE encapsulation, QoS, MPLS VPNs, and SSL/IPsec encryption/decryption, etc. From the perspective of the network device, services plane packets may have a transit destination IP address, or may have a receive destination IP address (for example, in the case of a VPN tunnel endpoint).
Reference: https://tools.cisco.com/security/center/resources/copp_best_practices
2025 Question 6:
Refer to the exhibit.

The network administrator configured VRF lite for customer The technician at the remote site misconfigured VRF on the router. Which configuration will resolve connectivity for both sites of customer a?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Correct Answer: D
From the exhibit, we learned:
+
VRF customer_a was exported with Route target (RT) of 1:1 so at the remote site it must be imported with the same RT 1:1.
+
VRF customer_a was imported with Route target (RT) of 1:1 so at the remote site it must be exported with the same RT 1:1.
Therefore at the remote site we must configure the command “route-target both 1:1” (which is equivalent to two commands “route-target import 1:1” and “route-target export 1:1”.
2025 Question 7:
Refer to the exhibit.
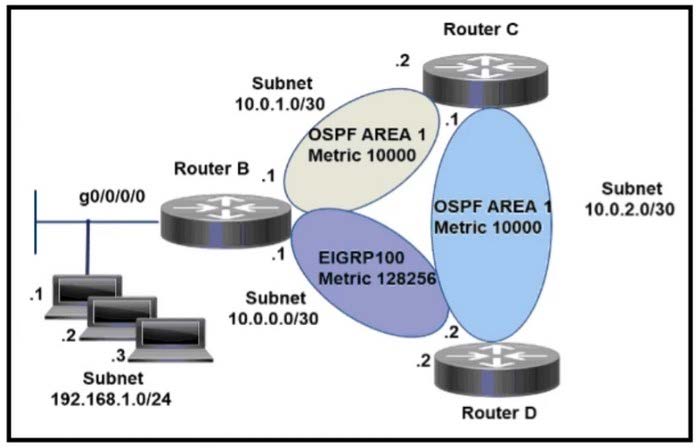
An engineer configures router B to direct all traffic from host 192.168.1.3 to router C. All other traffic must be routed through normal routing-protocol operations. Which configuration accomplishes the task?
A. interface g0/0/0 ip address 192.168.1.254 255.255.255.0 ! access-list 101 permit ip host 192.168.1.3 any access-list 101 permit ip any any ! route-map CCNP permit 10 match ip address 101 set ip next-hop 10.0.1.2
B. interface g0/0/0 ip address 192.168.1.254 255.255.255.0 ip policy route-map CCNP ! access-list 101 permit ip host 192.168.1.3 any ! route-map CCNP permit 10 match ip address 101 set ip next-hop 10.0.2.1
C. interface g0/0/0 ip address 192.168.1.254 255.255.255.0 ip policy route-map CCNP ! access-list 101 permit ip any host 192.168.1.3 ! route-map CCNP permit 10 match ip address 101 set ip next-hop 10.0.1.2
D. interface g0/0/0 ip address 192.168.1.254 255.255.255.0 ip policy route-map CCNP ! access-list 101 permit ip host 192.168.1.3 any ! route-map CCNP permit 10 match ip address 101 set ip next-hop 10.0.1.2
Correct Answer: D
2025 Question 8:
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is trying to block the route to 192.168.2.2 from the routing table by using the configuration that is shown. The route is still present in the routing table as an OSPF route. Which action blocks the route?
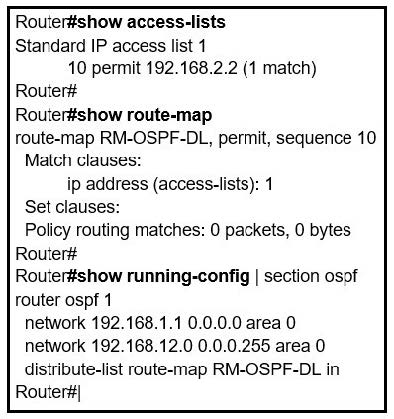
A. Use an extended access list instead of a standard access list.
B. Change sequence 10 in the route-map command from permit to deny.
C. Use a prefix list instead of an access list in the route map.
D. Add this statement to the route map: route-map RM-OSPF-DL deny 20.
Correct Answer: D
2025 Question 9:
Examine the exhibit.
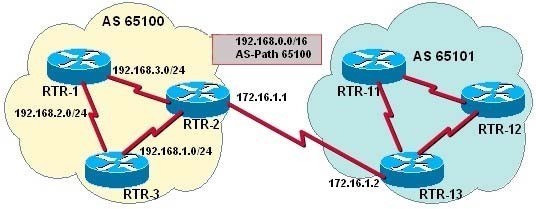
You have determined that RTR2 is not advertising the CIDR summary address 192.168.0.0 to the other routers in AS 65100.
Which set of configuration commands will enable the BGP router RTR2 to announce the network prefix 192.168.0.0/16 to the other routers in the AS 65100?
A. router bgp 65100 neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 65100 neighbor 192.168.3.2 remote-as 65100 network 192.168.3.0
B. router bgp 65100 neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 65101 neighbor 192.168.3.2 remote-as 65100 network 192.168.0.0
C. router bgp 65100 neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 65100 neighbor 192.168.3.2 remote-as 65100 network 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 ip route 192.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 null 0
D. router bgp 65100 neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 65101 neighbor 192.168.3.2 remote-as 65100 network 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0 null 0
Correct Answer: D
Issuing the following commands will cause RTR2 to advertise the CIDR block 192.168.0.0/16 to the other routers by using BGP:
RTR2(config)# router bgp 65100
RTR2(config-router)# neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 65101
RTR2(config-router)# neighbor 192.168.3.2 remote-as 65100
RTR2(config-router)# network 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
RTR2(config-router)# ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0 null 0 The network command specifies the address that will be inserted into the BGP table. Without the mask keyword, the classful network will be assumed. Because 255.255.0.0, or /16,
is not the natural mask for any Class C address, the mask keyword must also be specified. Thus, 192.168.0.0 and 255.255.0.0 identify the desired address and mask of the 192.168.0.0/16 network prefix.
The router checks the IP forwarding table for an exact match before it advertises the route. Without a matching entry in the IP forwarding table, that route will not be advertised. RTR2 must be able to advertise a CIDR block and not the
individual subnets. A static route is required because BGP requires that a match of the network prefix be present in the forwarding table when using the network command with the mask keyword. Therefore, to ensure an exact match for the
identified prefix exists in the IP forwarding table, and to ensure that the prefix will always be advertised, a static route for 192.168.0.0/16 to null 0 is also required.
The syntax for the network command is shown below:
network network-number [ mask network-mask ] [ route-map map-tag ]
The parameters are:
mask – This parameter is optional and identifies the network or subnetwork to advertise. route-map – This parameter is optional and identifies a preconfigured route-map that will be used to filter specific addresses from being advertised.
The following command set is missing the mask keyword in the network command and the command to create a static route to null 0. The address used in the network command is also incorrect. It should 192.168.0.0:
router bgp 65100
neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 65100
neighbor 192.168.3.2 remote-as 65100
network 192.168.3.0
The following command set is missing the mask keyword in the network command and the command to create a static route to null 0:
router bgp 65100
neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 65101
neighbor 192.168.3.2 remote-as 65100
network 192.168.0.0
The following command set uses an incorrect mask (255.0.0.0) in the command that creates the static route to null 0. It should be 255.255.0.0:
router bgp 65100
neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 65100
neighbor 192.168.3.2 remote-as 65100
network 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
ip route 192.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 null 0
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Describe, configure, and verify BGP peer relationships and authentication
References:
Internetworking Case Studies > Using the Border Gateway Protocol for Interdomain Routing > Controlling the Flow of BGP Updates > CIDR and Aggregate Addresses > Aggregation and Static Routes
2025 Question 10:
Refer to the exhibit.

An administrator configured a Cisco router for TACACS authentication, but the router is using the local enable password instead. Which action resolves the issue?
A. Configure the aaa authentication login default group admin local if-authenticated command instead.
B. Configure the aaa authentication login admin group tacacs+ local enable none command instead.
C. Configure the aaa authentication login admin group tacacs+ local if-authenticated command instead.
D. Configure the aaa authentication login admin group admin local enable command instead.
Correct Answer: D
2025 Question 11:
Refer to the exhibit.

A network engineer troubleshooting a packet drop problem for the host 172.16.100.5 notices that only one link is used and installed on the routing table, which saturates the bandwidth. Which action must the engineer take to resolve the high bandwidth utilization problem and share the traffic toward this host between the two available links?
A. Disable the eigrp split horizon loop protection mechanism.
B. Set the eigrp variance equal to 3 to install a second route with a metric not larger than 3 times of the best metric.
C. Change the EIGRP delay metric to meet the feasibility condition.
D. Set the eigrp variance equal to 4 to install a second route with a metric not larger than 4 times of the best metric.
Correct Answer: C
From the output of the “show ip eigrp topology …” command, we notice network 172.16.100.5/32 was learned via two routes:
+
From 10.4.1.5 with FD = 409600 and AD = 128256
+
From 10.3.1.6 with FD = 435200 and AD = 409600
To use both paths (called unequal cost load balancing) with EIGRP, the second path must satisfy the feasibility condition. The feasibility condition states that, the Advertised Distance (AD) of a route must be lower than the feasible distance of
the current successor route.
In this case, the second path did not satisfy the feasible condition as its AD (409600) is equal to the FD of the best path -> Therefore we cannot configure load balancing with “variance” command.
2025 Question 12:
Which command can be used to view the number of times the SPF algorithm has been executed?
A. show ip ospf
B. show ip ospf interface
C. show ip ospf database
D. show ip ospf neighbor
Correct Answer: A
The show ip ospf command can be used to view the number of times the SPF algorithm has been executed, as shown in the last line of the following output:
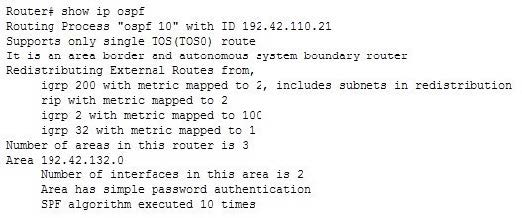
The show ip ospf interface command can be used to view neighbor adjacencies. A partial output of the command is shown below. It will not show the number of times the SPF algorithm has been executed.

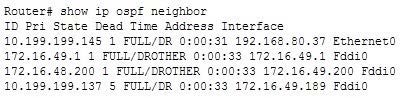
The show ip ospf neighbor command can also be used to view neighbor adjacencies, although its output is slightly different from the show ip ospf interface command. A partial output of the show ip ospf neighbor command is shown below. It also does not show the number of times the SPF algorithm was executed.
The show ip ospf database command does not show the number of times the SPF algorithm has executed. It shows the contents of OSPF database. Partial output is shown below:
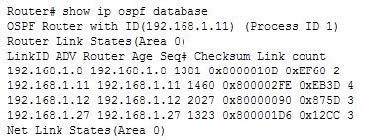
You can make the command output more specific by using parameters with the show ip ospf database command. For example, to view only Type 5 LSAs in the database, you would execute the show ip ospf database external command.
Since all Type 5 LSAs are from external networks, this keyword will trim the output to only those types of LSAs. When Type 5 (or external) routes are placed in the database, the next hop address will be 0.0.0.0, which makes it appear as if it is
a default route. What this really means is that any traffic that needs to go to that external network will be sent to the router that originated the advertisement (the ASBR).
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify OSPF operations
References:
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference > OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T > show ip ospf
2025 Question 13:
Refer to the exhibit.

R1 and R2 cannot establish an EIGRP adjacency. Which action establishes EIGRP adjacency?
A. Remove the current autonomous system number on one of the routers and change to a different value.
B. Remove the passive-interface command from the R2 configuration so that it matches the R1 configuration.
C. Add the no auto-summary command to the R2 configuration so that it matches the R1 configuration.
D. Add the passive-interface command to the R1 configuration so that it matches the R2 configuration.
Correct Answer: B
2025 Question 14:
What is the term used when it causes the packets to lose their MPLS labels including the VPN information that lies in the inner MPLS Label i.e. if a packet goes through an untagged interface, the VPN information is lost and VPN sites lose connectivity?
A. Pseudowire
B. Black Hole
C. Traffic Engineering
D. Active Network Abstraction
Correct Answer: B
2025 Question 15:
You are configuring EIGRP on a spoke router in a hub-and-spoke topology. In an effort to keep the routing table small, the hub router has been configured to send only a default route to the remote routers.
What command would you use on the spoke routers to enable them to send only connected and summary routes to the hub router, and prevent the hub router from sending a query to the spoke router when a route is lost elsewhere?
A. eigrp stub
B. eigrp stub static
C. eigrp passive
D. eigrp stub receive-only
Correct Answer: A
The eigrp stub command is used to configure a router to send only connected and summary routes to its neighboring router.
For example, examine the following output of the show ip route command that was executed on a router configured as a stub router:
router10#show ip route
C 172.16.5.0/24 is directly connected, Serial 0
D 192.168.7.0/24 [90/16523564] via 172.16.4.1, 00:21:20, Serial 1 D 172.16.0.0/16 is a summary, 00:21:23, Null 0
C 172.16.4.0/24 is directly connected, Serial 2
The routes that will be advertised are 172.16.5.0/24, 172.16.4.0/24, and the summary route 172.16.0.0/16. The first two is directly connected routes, and the last is the summary route that is auto configured by the EIGRP process.
When the stub feature is enabled on a router, the router will announce itself as a stub router. Neighbor routers will not query a stub router for alternate routes when a route is lost elsewhere in the network.
The EIGRP stub feature works well in hub-and-spoke topologies when the goal is to minimize the amount of EIGRP bandwidth and processing associated with the spoke router. The eigrp stub command has the following syntax:
eigrp stub [receive-only | connected | static | summary]
When you do not specify any keywords with the command, connected and summary are used by default. receive-only: Prevents the router from sending any connected or summary routes.
connected: Instructs the router to send connected routes.
static: Instructs the router to send static routes that were redistributed by using the redistribute static command.
summary: Instructs the router to send summary routes.
These parameters can be combined to resolve various problems, as seen in the following image:
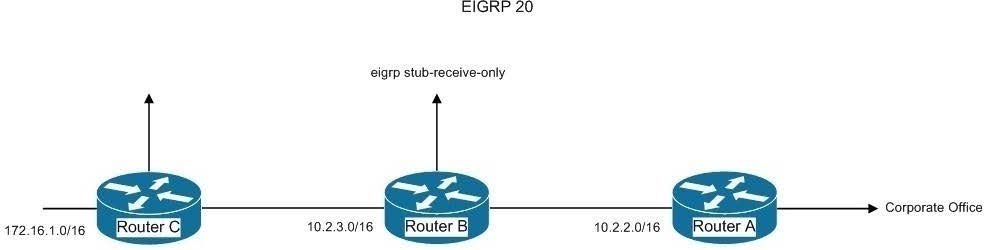
Router A is not receiving the route to the 172.16.1.0/16 network because Router B, which stands between Router A and C, is configured with the eigrp stub-receive-only command.
This is resulting in hosts from the corporate office being unable to connect to hosts in the 172.16.0.0/16 network.
If there were a legitimate reason to keep Router B configured with the eigrp stub-receive-only command, the problem could be solved by executing the following command set on Router A:
routerA(config)# router eigrp 20
routerA(config-router)# ip summary-address eigrp 20 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 routerA(config-router)# eigrp stub connected summary
This command set would create a summary address for the 172.16.0.0/16 network and then advertise it to the corporate office as a result of using the eigrp stub connected summary command. The inclusion of the connected parameter
ensures that the directly connected networks will also be advertised, to ensure that hosts in the corporate office can reach the 172.16.0.0/16 network.
The eigrp stub static command instructs the router to send static routes that were redistributed by using the redistribute static command. Examine the EIGRP configuration shown below:
ip route 10.4.4.0 255.255.255.0 10.4.3.10
Route eigrp 200
No auto-summary
Redistribute static 1000 1 255 1 1500
Network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.3.
Network 10.4.2.0 0.0.0.255
Eigrp stub static
With this configuration, the router would not advertise any of the networks defined in the network statements, but would only advertise the static route configured with the line ip route 10.4.4.0 255.255.255.0 10.4.3.10.
Eigrp passive is not a valid Cisco command.
Eigrp stub receive-only will cause the router to not advertise any routes. The router will only receive updates.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify EIGRP stubs
References:
Cisco IOS Master Command List, Release 12.4 > e through h > eigrp stub
…
You can download the free Cisco 300-410 PDF or practice the latest Cisco 300-410 exam dumps online. These dumps can help you improve your skills, but they cannot truly help you pass the Cisco 300-410 ENARSI exam.
We recommend downloading the latest released Leads4pass 300-410 dumps here: https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html (including 925 Q\&As and the latest 2025 simulated labs). This will truly help you successfully pass the Cisco 300-410 ENARSI exam.