leads4pass 300-410 Dumps latest version contains 608 exam questions and answers (Including 2022 Newest Simulation Labs), and fixes previous errors, for candidates preparing for the 300-410 ENARSI exam.
Welcome to download the latest version of 300-410 Dumps: https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html (Include 2022 Newest Simulation Labs) and practice the 300-410 ENARSI exam questions using the PDF exam files and VCE simulation engine to help you win.
Check out the Cisco 300-410 PDF available free of charge in 2022:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1B-r4PbrEKNrBNRiN6uIllaijaHFPkqMk/view?usp=sharing
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1C3Ny7fnTfs5Vn0f2RRHfve8ZUyogbf9m/view?usp=sharing
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1GA7Ozk2bKTyvwBiVoCyMSk2jVZ43AD2H/view?usp=sharing
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Hmd2m8IlFiln0lDicik9brJDd0T1caJr/view?usp=sharing
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Q5zIxqFRkF6FTyIj-xj2Q0nWn4J5Eg_X/view?usp=sharing
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1k425tFP4HR9seCaxmeEkIuaYcXKIU7rk/view?usp=sharing
Check out the Cisco 300-410 dumps exam questions and answers available in the new release (Free part 2022 Newest Simulation Labs):
| Number of exam questions | Exam name | From | Release time |
| 15 | Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI) | leads4pass | Oct 04, 2022 |
New Question 1:
Refer to the exhibit. Users in the branch network of 2001:db8:0:4::/64 report that they cannot access the Internet. Which command is issued in IPv6 router EIGRP 100 configuration mode to solve this issue?
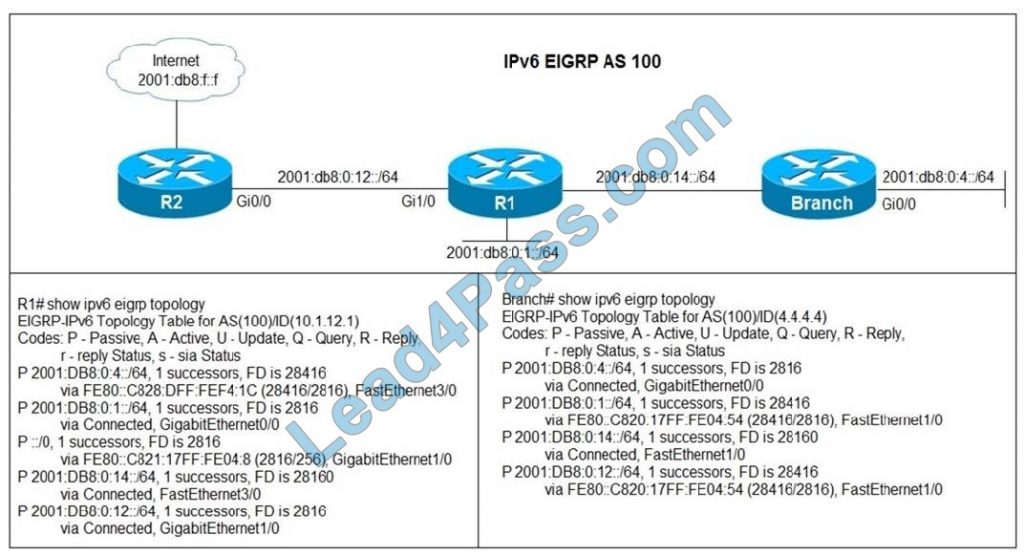
A. Issue the eigrp stub command on R1.
B. Issue the no eigrp stub command on R1.
C. Issue the eigrp stub command on R2.
D. Issue the no eigrp stub command on R2.
Correct Answer: B
New Question 2:
Refer to the exhibit. Which configuration configures a policy on R1 to forward any traffic that is sourced from the 192.168.130.0/24 network to R2?
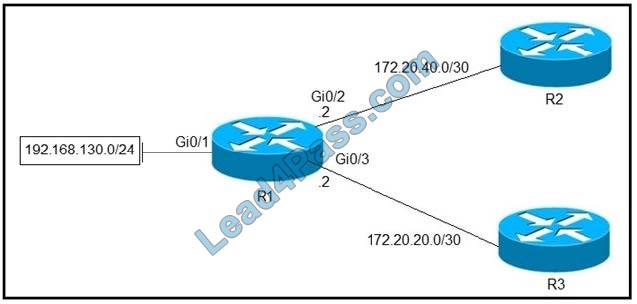
A. access-list 1 permit 192.168.130.0 0.0.0.255 ! interface Gi0/2 IP policy route-map test! route-map test permit 10 match IP address 1 set IP next-hop 172.20.20.2
B. access-list 1 permit 192.168.130.0 0.0.0.255 ! interface Gi0/1 IP policy route-map test! route-map test permit 10 match IP address 1 set IP next-hop 172.20.40.2
C. access-list 1 permit 192.168.130.0 0.0.0.255 ! interface Gi0/2 IP policy route-map test! r oute-map test permit 10 match IP address 1 set IP next-hop 172.20.20.1
D. access-list 1 permit 192.168.130.0 0.0.0.255 ! interface Gi0/1 IP policy route-map test! route-map test permit 10 match IP address 1 set IP next-hop 172.20.40.1
E. access-list 1 permit 192.168.130.0 0.0.0.255 ! interface Gi0/1 IP policy route-map test! route-map test permit 10 match IP address 1 set IP next-hop 172.20.20.1
Correct Answer: E
New Question 3:
R2 has a locally originated prefix 192.168.130.0/24 and has these configurations: What is the result when the route-map OUT command is applied toward an eBGP neighbor R1 (1.1.1.1) by using the neighbor 1.1.1.1 route-map OUT out command?

A. R1 sees 192.168.130.0/24 as two AS hops away instead of one AS hop away.
B. R1 does not accept any routes other than 192.168.130.0/24
C. R1 does not forward traffic that is destined for 192.168.30.0/24
D. Network 192.168.130.0/24 is not allowed in the R1 table
Correct Answer: A
New Question 4:
Which method changes the forwarding decision that a router makes without first changing the routing table or influencing the IP data plane?
A. nonbroadcast multiaccess
B. packet switching
C. policy-based routing
D. forwarding information base
Correct Answer: C
New Question 5:
Refer to the exhibit. The output of the traceroute from R5 shows a loop in the network. Which configuration prevents this loop?
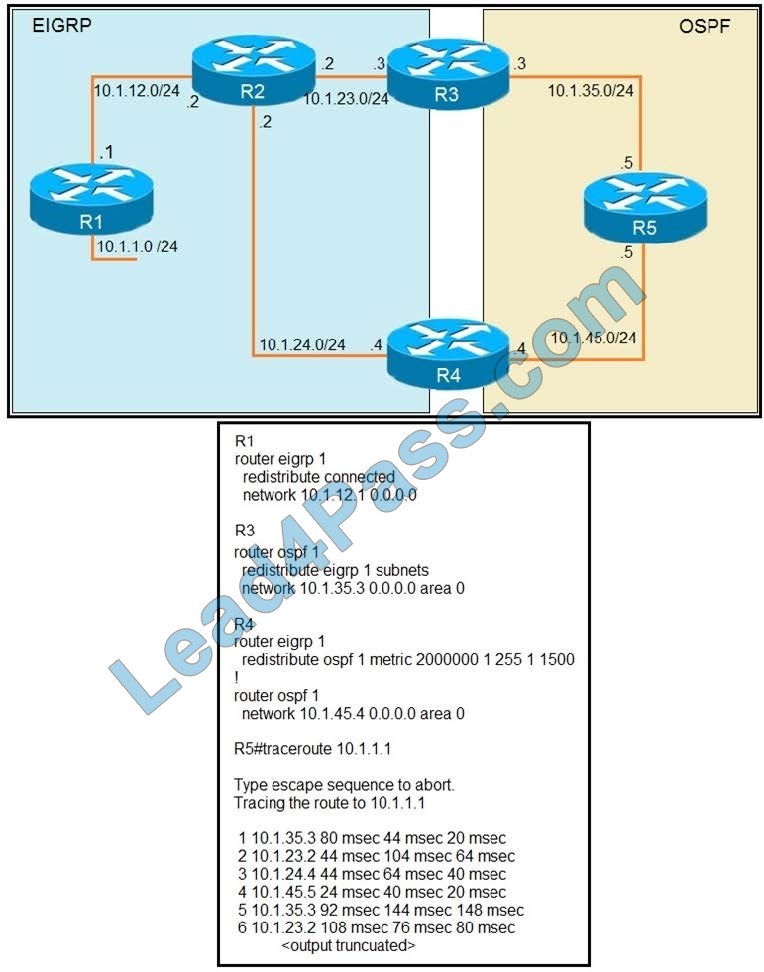

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Correct Answer: A
New Question 6:
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer configures a static route on a router, but when the engineer checks the route to the destination, a different next hop is chosen. What is the reason for this?
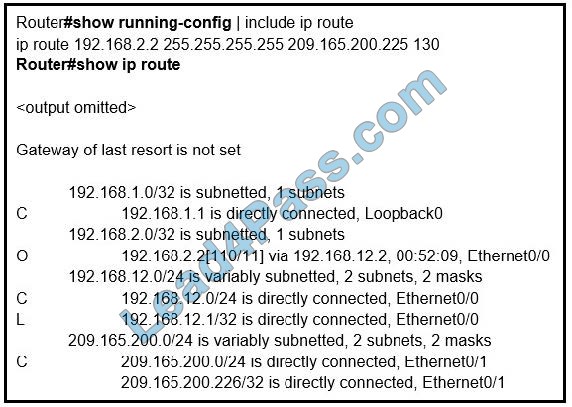
A. Dynamic routing protocols always have priority over static routes.
B. The metric of the OSPF route is lower than the metric of the static route.
C. The configured AD for the static route is higher than the AD of OSPF.
D. The syntax of the static route is not valid, so the route is not considered.
Correct Answer: C
The AD of the static route is manually configured to 130 which is higher than the AD of the OSPF router which is 110.
New Question 7:
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is trying to generate a summary route in OSPF for network 10.0.0.0/8, but the summary route does not show up in the routing table. Why is the summary route missing?
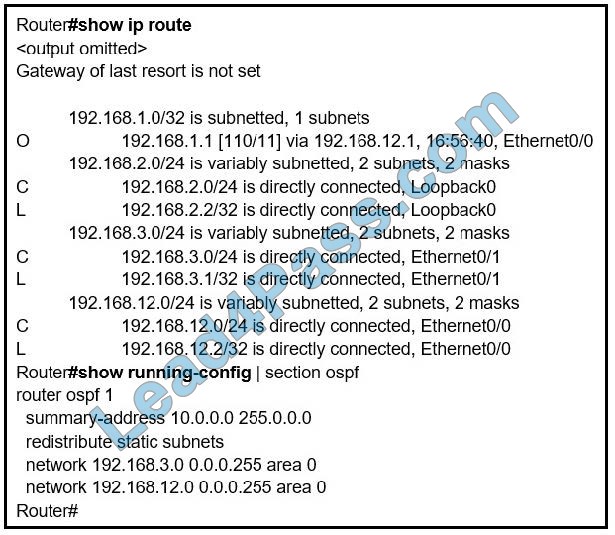
A. The summary-address command is used only for summarizing prefixes between areas.
B. The summary route is visible only in the OSPF database, not in the routing table.
C. There is no route for a subnet inside 10.0.0.0/8, so the summary route is not generated.
D. The summary route is not visible on this router, but it is visible on other OSPF routers in the same area.
Correct Answer: C
The summary address is only used to create aggregate addresses for OSPF at an autonomous system boundary.
It means this command should only be used on the ASBR when you are trying to summarize externally redistributed routes from another protocol domain or you have an NSSA area. But a requirement to create a summarized route is:
The ASBR compares the summary route\’s range of addresses with all routes redistributed into OSPF on that ASBR to find any subordinate subnets (subnets that sit inside the summary route range). If at least one subordinate subnet exists,
the ASBR advertises the summary route.
New Question 8:
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is trying to block the route to 192.168.2.2 from the routing table by using the configuration that is shown. The route is still present in the routing table as an OSPF route. Which action blocks the route?
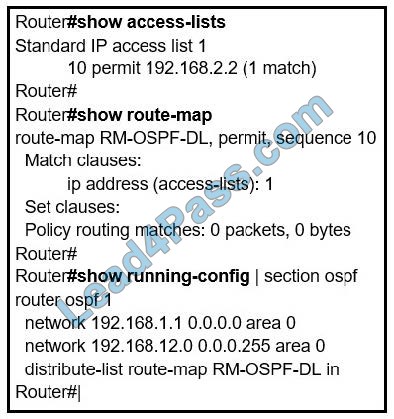
A. Use an extended access list instead of a standard access list.
B. Change sequence 10 in the route-map command from permit to deny.
C. Use a prefix list instead of an access list in the route map.
D. Add this statement to the route map: route-map RM-OSPF-DL deny 20.
Correct Answer: B
New Question 9:
What is a prerequisite for configuring BFD?
A. Jumbo frame support must be configured on the router that is using BFD.
B. All routers in the path between two BFD endpoints must have BFD enabled.
C. Cisco Express Forwarding must be enabled on all participating BFD endpoints.
D. To use BFD with BGP, the timers 3 9 commands must first be configured in the BGP routing process.
Correct Answer: C
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/12_0s/feature/guide/fs_bfd.html#wp1043332
New Question 10:
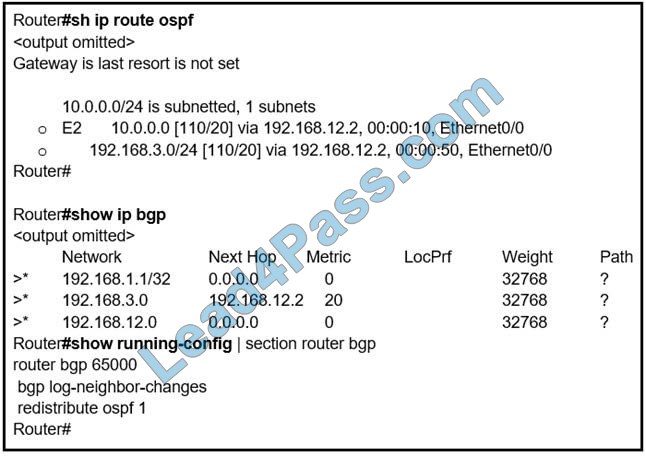
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is trying to redistribute OSPF to BGP, but not all of the routes are redistributed. What is the reason for this issue?
A. By default, only internal routes and external type 1 routes are redistributed into BGP
B. Only classful networks are redistributed from OSPF to BGP
C. BGP convergence is slow, so the route will eventually be present in the BGP table
D. By default, only internal OSPF routes are redistributed into BGP
Correct Answer: D
If you configure the redistribution of OSPF into BGP without keywords, only OSPF intra-area and inter-area routes are redistributed into BGP, by default.
You can redistribute both internal and external (type-1 and type-2) OSPF routes via this command:
Router(config-router)#redistribute ospf 1 match internal external 1 external 2
New Question 11:
Refer to the exhibit.
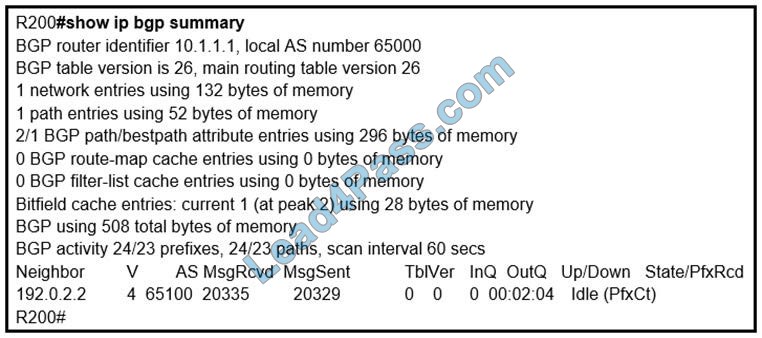
In which circumstance does the BGP neighbor remain in idle condition?
A. if prefixes are not received from the BGP peer
B. if prefixes reach the maximum limit
C. if a prefix list is applied in the inbound direction
D. if prefixes exceed the maximum limit
Correct Answer: D
New Question 12:
Which attribute eliminates LFAs that belong to protected paths in situations where links in a network are connected through a common fiber?
A. Shared Risk Link Group (SRLG)-disjoint
B. linecard-disjoint
C. lowest-repair-path-metric
D. interface-disjoint
Correct Answer: A
LFA Tie-Breaking Rules
When there are multiple candidate LFAs for a given primary path, EIGRP uses a tie-breaking rule to select one LFA per primary path per prefix. A tie-breaking rule considers LFAs that satisfy certain conditions or have certain attributes. EIGRP uses the following four attributes to implement tie-breaking rules:
–
Interface-disjoint—Eliminates LFAs that share the outgoing interface with the protected path.
–
Linecard-disjoint—Eliminates LFAs that share the line card with the protected path.
–
Lowest-repair-path-metric—Eliminates LFAs whose metric to the protected prefix is high. Multiple LFAs with the same lowest path metric may remain in the routing table after this tie-breaker is applied.
–
Shared Risk Link Group (SRLG)-disjoint—Eliminates LFAs that belong to any of the protected path SRLGs. SRLGs refer to situations where links in a network share a common fiber (or a common physical attribute). If one link fails, other links in the group may also fail. Therefore, links in a group share risks.
New Question 13:
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer is troubleshooting BGP on a device but discovers that the clock on the device does not correspond to the time stamp of the log entries. Which action ensures consistency between the two times?
A. Configure the service timestamps log uptime command in global configuration mode.
B. Configure the logging clock synchronize command in global configuration mode.
C. Configure the service timestamps log DateTime localtime command in global configuration mode.
D. Make sure that the clock on the device is synchronized with an NTP server.
Correct Answer: C
The Time zone needs to be changed. default it UTC Central European Time (CET)
New Question 14:
Refer to the exhibit. What is the result of applying this configuration?
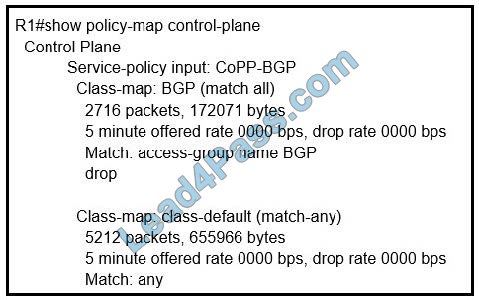
A. The router can form BGP neighborships with any other device.
B. The router cannot form BGP neighborships with any other device.
C. The router cannot form BGP neighborships with any device that is matched by the access list named “BGP”.
D. The router can form BGP neighborships with any device that is matched by the access list named “BGP”.
Correct Answer: C
After the BGP session is UP. I configured the CoPP to drop 10.3.3.3 BGP traffic (R3). R3 BGP traffic that matched the ACL 100 is dropped and the state is in IDLE ——————————————– access-list 100 permit TCP host 10.3.3.3 any eq BGP access-list 100 permit TCP host 10.3.3.3 eq bgp any! class-map match-all class-BGP match access-group 100! policy-map policy-bgp class class-bgp drop ! control-plane service-policy input policy-BGP! The 10.3.3.3 neighbor goes to IDLE
New Question 15:
Which command displays the IP routing table information that is associated with VRF-Lite?
A. show ip vrf
B. show IP route vrf
C. show run vrf
D. show IP protocols vrf
Correct Answer: B
…
You can download the free Cisco 300-410 PDF and study the Cisco 300-410 exam questions online. These will help you grow, but will not help you actually pass the Cisco 300-410 ENARSI Exam.
Welcome to download the newly released leads4pass 300-410 Dumps: https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html (608 Q&A) (Include 2022 Newest Simulation Labs), which really help you to successfully pass the Cisco 300-410 ENARSI Exam.
